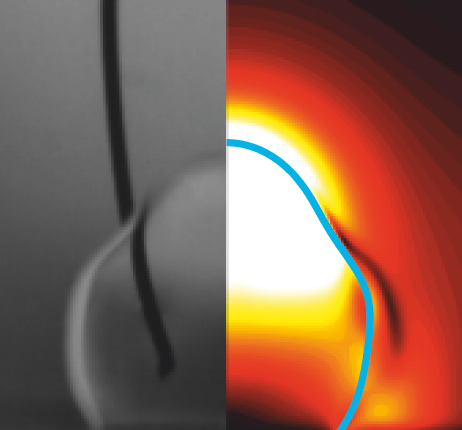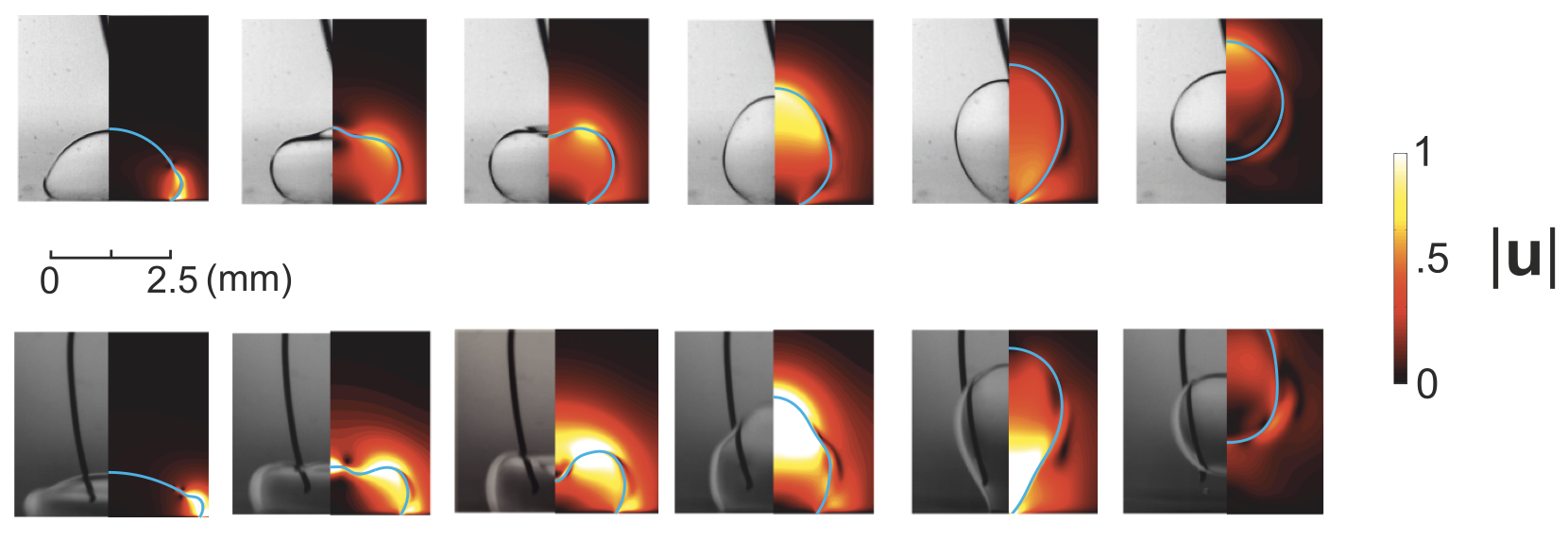
A deformed droplet may leap from a solid substrate, impelled to detach through the conversion of surface energy into kinetic energy that arises as it relaxes to a sphere. Electrowetting provides a means of preparing a droplet on a substrate for lift-off. When a voltage is applied between a water droplet and a dielectric-coated electrode, the wettability of the substrate increases in a controlled way, leading to the spreading of the droplet. Once the voltage is released, the droplet recoils, due to a sudden excess in surface energy, and droplet detachment may follow. The process of drop detachment and lift-off, prevalent in both biology and micro-engineering, has to date been considered primarily in terms of qualitative scaling arguments for idealized superhydrophobic substrates. We here consider the eletrically-induced ejection of droplets from substrates of finite wettability and analyze the process quantitatively. We compare experiments to numerical simulations and analyze how the energy conversion efficiency is affected by the applied voltage and the intrinsic contact angle of the droplet on the substrate. Our results indicate that the finite wettability of the substrate significantly affects the detachment dynamics, and so provide new rationale for the previously reported large critical radius for drop ejection from micro-textured substrates.