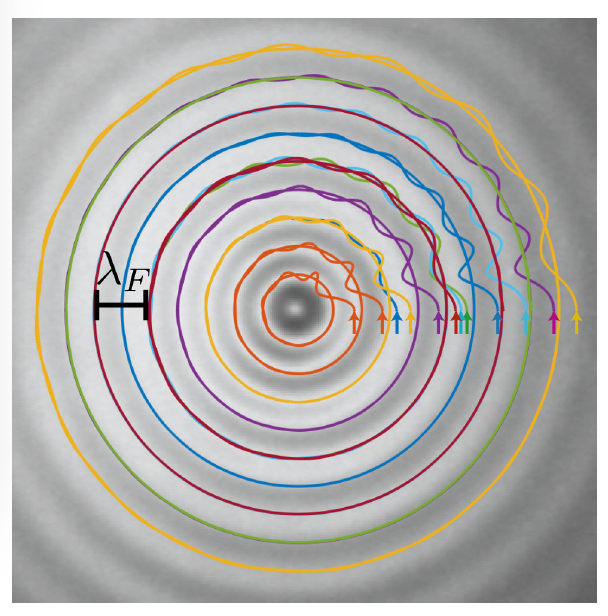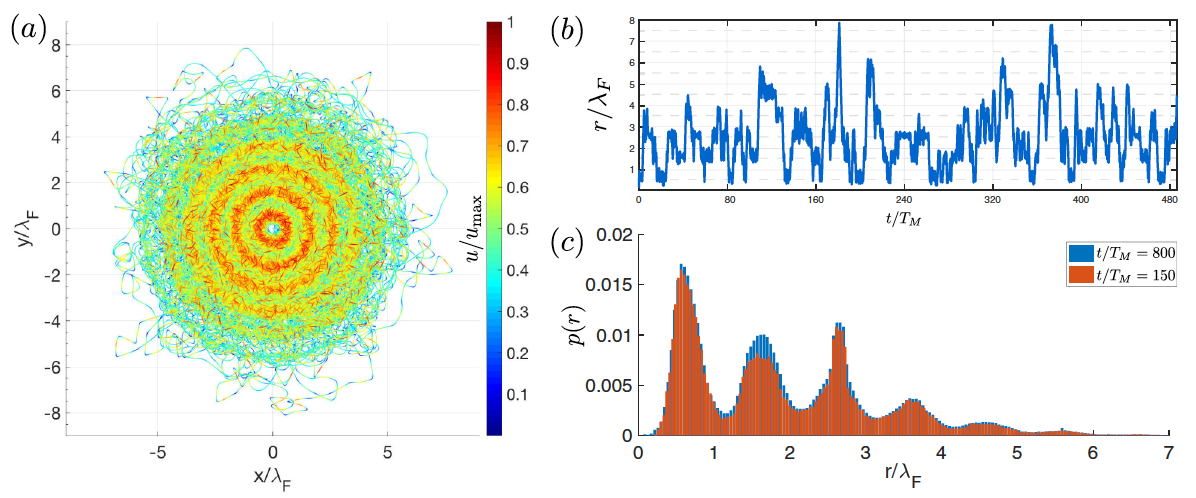
We explore the effects of an imposed potential with both oscillatory and quadratic components on the dynamics of walking droplets.We first conduct an experimental investigation of droplets walking on a bath with a central circular well. The well acts as a source of Faraday waves, which may trap walking droplets on circular orbits. The observed orbits are stable and quantized, with preferred radii aligning with the extrema of the well-induced Faraday wave pattern. We use the stroboscopic model of Oza et al. (2013) with an added potential to examine the interaction of the droplet with the underlying well-induced wavefield. We show that all quantized orbits are stable for low vibrational accelerations. Smaller orbits may become unstable at higher forcing accelerations and transition to chaos through a path reminiscent of the Ruelle-Takens-Newhouse scenario. We proceed by considering a generalized pilot-wave system in which the relative magnitudes of the pilot-wave force and drop inertia may be tuned. When the drop inertia is dominated by the pilotwave force, all circular orbits may become unstable, with the drop chaotically switching between them. In this chaotic regime, the statistically stationary probability distribution of the drop’s position reflects the relative instability of the unstable circular orbits. We compute the mean wavefield from a chaotic trajectory and confirm its predicted relationship with the particle’s probability density function.
See paper: Tambasco, L.D. and Bush, J.W.M. Chaos (2018)